Multiple Choice
Identify the choice that best completes the
statement or answers the question.
|
|
|
1.
|
The variable plotted on the horizontal or x-axis is called the
____.
a. | dependent variable | c. | variable with the largest range | b. | independent
variable | d. | variable with the
smallest range |
|
|
|
2.
|
A rule or principle that describes what happens in nature is a ____.
a. | hypothesis | c. | scientific law | b. | problem | d. | theory |
|
|
|
3.
|
An explanation of an event that is based on repeated observations and
experiments is a ____.
a. | hypothesis | c. | problem | b. | scientific law | d. | theory |
|
|
|
4.
|
A factor in an experiment that changes from the manipulation of the independent
variable is the ____.
a. | constant | c. | dependent variable | b. | control | d. | hypothesis |
|
|
|
5.
|
A factor that does NOT change in an experiment is the ____.
a. | constant | c. | dependent variable | b. | control | d. | hypothesis |
|
|
|
6.
|
Studying the effect of one thing on another in order to test a hypothesis is
a(n) ____.
a. | exercise | c. | constant | b. | experiment | d. | problem |
|
|
|
7.
|
If you ride your bicycle down a straight road for 500 m then turn around and
ride back, your distance is ____ your displacement.
a. | greater than | c. | less than | b. | equal to | d. | can’t
determine |
|
|
|
8.
|
Motion is a change in ____.
a. | time | c. | velocity | b. | speed | d. | position |
|
|
|
9.
|
The relationship among speed, distance, and time is ____.
a. | t = s/d | c. | s = dt | b. | d = t/s | d. | s = d/t |
|
|
|
10.
|
A single point on a distance-time graph tells the ____.
a. | instantaneous speed | c. | constant speed | b. | average speed | d. | average
velocity |
|
|
|
11.
|
Acceleration is rate of change of ____.
a. | position | c. | velocity | b. | time | d. | force |
|
|
|
12.
|
The equation used to find acceleration is a = ____.
a. | vf – vi/t | c. | vi –
vf /t | b. | v/t | d. | vi +
vf/t |
|
|
|
13.
|
A horizontal line on a velocity/time graph shows ____ acceleration.
a. | positive | c. | changing | b. | negative | d. | zero |
|
|
|
14.
|
Inertia varies depending on ____.
a. | force | c. | velocity | b. | mass | d. | motion |
|
|
|
15.
|
The relationship among mass, force, and acceleration is explained by
____.
a. | conservation of momentum | c. | Newton's second law of
motion | b. | Newton's first law of motion | d. | Newton's third law of
motion |
|
|
|
16.
|
A feather will fall through the air more slowly than a brick because of
____.
a. | air resistance | c. | inertia | b. | gravity | d. | momentum |
|
|
|
17.
|
In the absence of air, a penny and a feather that are dropped from the same
height at the same time will ____.
a. | fall at different rates | c. | float | b. | fall at the same
rate | d. | not have
momentum |
|
|
|
18.
|
The acceleration due to gravity is ____.
a. | 98 m/s2 | c. | 9.8 m/s | b. | 9.8 m/s2 | d. | 0.98 m/s |
|
|
|
19.
|
According to Newton's second law of motion, ____.
a. | F = m × a | c. | F = p
× a | b. | F = m ×
v | d. | F =
p × v |
|
|
|
20.
|
When an object moves in a circular path, it accelerates toward the center of the
circle as a result of ____.
a. | centripetal force | c. | gravitational force | b. | frictional force | d. | momentum |
|
|
|
21.
|
For any object, the greater the force that's applied to it, the greater its
____ will be.
a. | acceleration | c. | inertia | b. | gravity | d. | velocity |
|
|
|
22.
|
The size of the gravitational force between two objects depends on their
____.
a. | frictional forces | b. | inertia | c. | masses and the
distance between them | d. | speed and
direction |
|
|
|
23.
|
When a force is exerted on a box, an equal and opposite force is exerted by the
box. These forces are called ____ forces.
a. | action-reaction | c. | frictional | b. | centripetal | d. | gravitational |
|
|
|
24.
|
In the equation p = m × v,
the p represents ____.
a. | friction | c. | momentum | b. | inertia | d. | position |
|
|
|
25.
|
The unit of momentum is ____.
a. | kg × m | c. | kg × m/s2 | b. | kg ×
m/s | d. | m/s2 |
|
|
|
26.
|
When two balls collide, the momentum of the balls after the collision is
explained by ____.
a. | the law of conservation of momentum | b. | Newton's first law of
motion | c. | Newton's second law of motion | d. | Newton's third law of
motion |
|
|
|
27.
|
An object that is in free fall seems to be ____.
a. | not moving | c. | speeded up by air resistance | b. | slowed by air
resistance | d. | weightless |
|
|
|
28.
|
If gravity did NOT affect the path of a horizontally thrown ball, the ball would
____.
a. | go straight up | c. | follow a curved path | b. | fall straight down | d. | travel
horizontally |
|
|
|
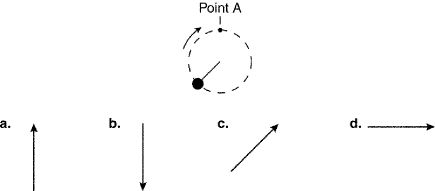 Figure
3-1
|
|
|
29.
|
A ball attached to a string is being swung in a clockwise circular path as shown
in Figure 3-1. Assume the string breaks at point A. In which direction will the ball be traveling an
instant later?
a. | direction a | c. | direction c | b. | direction b | d. | direction d |
|
|
|
30.
|
A ball attached to a string is being swung in a clockwise circular path as shown
in Figure 3-1. In which direction will the acceleration on the ball be when the ball passes point
A?
a. | direction a | c. | direction c | b. | direction b | d. | direction d |
|
|
|
31.
|
All except one of the following require the application of a net force.
Which one is the exception?
a. | to change an object from a state of rest to a state of motion. | d. | to maintain an
object in uniform circular motion. | b. | to maintain an object in motion at a constant
velocity. | e. | to change an
object’s direction of motion without changing its speed. | c. | to change an
object’s speed without changing its direction of motion. |
|
|
|
32.
|
A car rounds a curve while maintaining constant speed. The correcrt statement
is:
a. | The accelerations of the car is zero. | b. | The velocity of the car is
zero. | c. | No net force acts on the car. | d. | The velocity of the car is
constant. | e. | A net force acts upon the car. |
|
|
|
33.
|
A block of mass 5.0 kg is acted upon by a single force, producing an
acceleration of 2.0 m/s2. The force has a value of
a. | 5.0 N | c. | 2.5 N | b. | 10.0 N | d. | 0.5 N |
|
|
|
34.
|
A child, whose weight is 150 newtons, lifts a pumkin from the ground with a
force of 50 newtons. The force the pumkin exerts on the child is
a. | zero | b. | greater than zero, but less than 50
newtons | c. | 50 newtons | d. | more than 50
newtons |
|
|
|
35.
|
Your weight is 100 lb. Suppose you are standing on a scale in an elevator moving
up with a constant speed of 3 m/s. What would be the reading on the scale.
a. | 100 lb | b. | 130 lb | c. | 70
lb | d. | 30 lb | e. | 0 |
|
|
|
36.
|
The conservation of momentum is most closely related to
a. | Newton’s first law. | b. | Newton’s second law. | c. | Newton’s third
law. |
|
|
|
37.
|
What does an object have when moving that it doesn’t have when at
rest?
a. | momentum | b. | energy | c. | mass | d. | inertia | e. | none of
these |
|
|
|
38.
|
The SI unit for energy is the ____.
a. | calorie | c. | meter per second | b. | joule | d. | kilogram |
|
|
|
39.
|
You can calculate kinetic energy by using the equation ____.
a. | KE (J) = m (kg) × 9.8 m/s2
× h (m) | b. | KE (J) = w (m) × h (m) | c. | KE (J) = 1/2 m (kg) × v2 (m2/s2) | d. | KE (J) = 9.8
m/s2 × 1/2 m (kg) |
|
|
|
40.
|
You can calculate gravitational potential energy by using the equation
____.
a. | GPE (J) = 1/2m (kg) × 1/2h
(m) | b. | GPE (J) = m (kg) × 9.8 m/s2 × h (m) | c. | GPE (J) = h (m) × 9.8 m/s2 | d. | GPE (J) = 1/2h (m) × w (m) |
|
|
|
41.
|
In a nuclear fusion reaction, mass is transformed into ____.
a. | matter | c. | energy | b. | nuclei | d. | light |
|
|
|
42.
|
According to the law of conservation of energy, the total amount of energy in
the universe ____.
a. | remains constant | c. | increases | b. | changes constantly | d. | decreases |
|
|
|
43.
|
A material that reduces the flow of heat by conduction, convection, and
radiation is ____.
a. | a conductor | c. | an insulator | b. | condensation | d. | a solar
collector |
|
|
|
44.
|
Energy from the Sun travels to Earth as ____.
a. | chemical energy | c. | radiant energy | b. | combustion | d. | mechanical
energy |
|